FairBase (Fungal A-to-I RNA editing dataBase) is the first fungal A-to-I RNA editing database. It includes a comprehensive collection of A-to-I editing sites in six filamentous fungi, together with extensive annotations for each editing site. In FairBase, users can conveniently search editing sites and obtain editing levels for each editing site in various RNA-seq samples. In addition, the pathways involving RNA editing are built in FairBase to help users to understand the function of RNA editing. Furthermore, each fungus is equipped with a genome browser (JBrowse) that allows users to explore A-to-I editing in genomic context.
User-friendly web interfaces are designed for users to access the FairBase database. Data retrieve can be achieved in the Search, Blast and Pathway page and the retrieved editing sites are listed in a sortable and downloadable results table below. The complete description of editing site can be shown in the detail page page . All editing sites and editing events can be explored in genome context through JBrowse genome browser.
In the Search page, users must firstly select single or multiple fungal species in the species listbox as search objects. Then identifiers of genome reference sequences or chromosomes with A-to-I editing sites of selected fungal species will be listed in the chromosome listbox. If users want to search editing sites in whole-genome region, the "Any" item in the chromosome listbox should be selected. Users can define two extra conditions to restrict retrieval results to the editing sites of interest:
(1) Gene: A-to-I editing sites located in some specified genes can be picked out from the retrieval results by setting gene symbols and function annotation such as Pfam and GO terms. If users want to set multiple gene symbols (or functional terms) at the same time in one query, the multiple symbols (or functional terms) should be separated by vertical bars (for examples, "DHS|Tri1|nat1|DHS|Ve1|Cbh-C", "PF01916|PF00067", "GO:0005506|GO:0016705").
(2) Context: The editing sites located in specified genomic context can be picked out from the retrieval results. According to genome context, A-to-I editing sites can be classified into four types including 5'UTR, CDS, 3'UTR, Intron and Intergenic. The selections for "AA change" will appear for users to search "Nonsynonymous" or "Synonymous" editing sites when "CDS" is activated.
In the blast page, it also is mandatory to firstly select single or multiple fungal species before searching for A-to-I editing sites. First, users should specify a blast program (blastn, blastp or blastx), a sequence database (cDNA, gene, CDS or protein) and set some parameters including E-value, word size, gap cost, match, and mismatch score. Then, users should fill a nucleic acid or amino acid sequence in FASTA format into the sequence text area.
In the pathway page, users can search editing sites by KEGG pathway. After users specify a species, all edited pathways of this species will be listed in the drop down box.
After users submit a request, edited enzymes in specified pathway are tagged with red background. The editing sites occurred in an enzymes can be picked out from retrieval result table below by its identifiers.
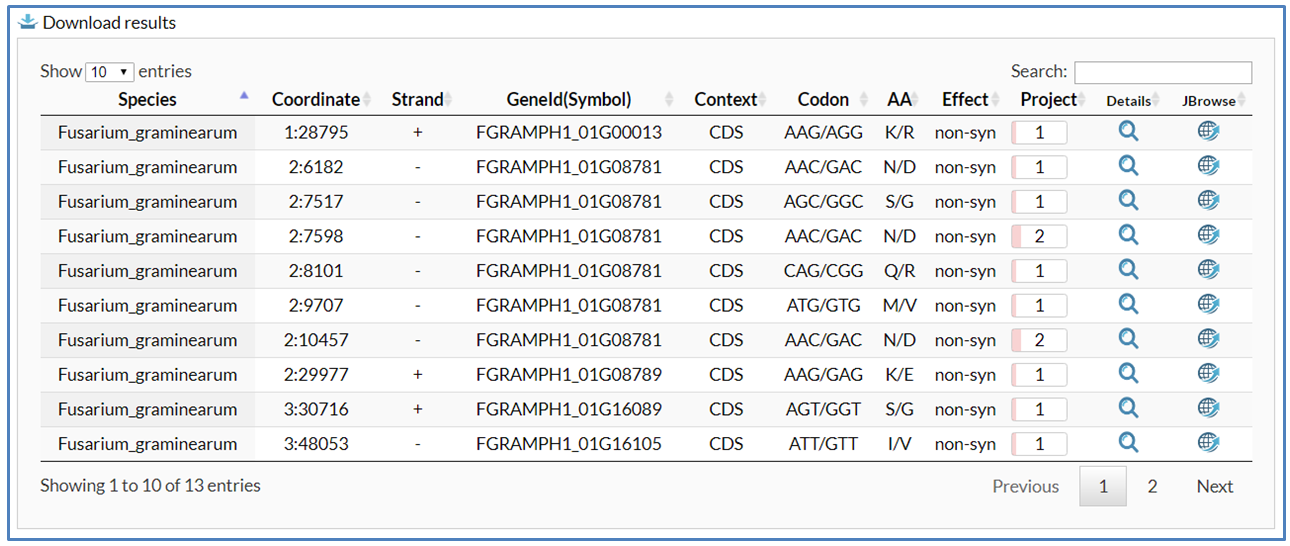
After users submit a search request in the search, blast and pathway pages, the searched editing sites are listed below in a retrieval result table. Users can download the retrieval results for downstream analyses, dynamically modify the number of showing editing sites per page to re-show results and enter keywords to choose more interesting editing sites from the retrieval results table. In the retrieval results table, at least 11 columns of information are provided for each editing site:
(1) Species to show which fungus is selected.
(2) Coordinate to show genomic position of editing site including chromosome and coordinate.
(3) Strand to show orientation of editing site.
(4) Gene Id (Symbol) to show identifier and symbol (if any) of edited gene. If users hover over gene Id, a box appears with gene functional annotaion including Pfam and GO terms.
(5) Context to show genomic context of editing site. Genomic contexts are classified into five types such as 5'UTR, CDS, 3'UTR, Intron and Intergenic.
(6) Codon to show edited codon. The codons before and after editing are separated by a slash.
(7) AA to show edited amino acid.The amino acids before and after editing are separated by a slash.
(8) Effect to show the editing effect of recoding in coding region, e.g. synonymous and nonsynonymous.
(9) Study to show number of BioProject in which site appears to be edited. It is showed by a progression bar.
(10) Details icon (![]() ) with hyperlink for opening the editing detail page to show more editing detail. For more details on the Detail page, refer to the Detail page section.
) with hyperlink for opening the editing detail page to show more editing detail. For more details on the Detail page, refer to the Detail page section.
(11) JBrowse icon (![]() ) with hyperlink for opening JBrowse to show editing site in genomic context. For more details on JBrowse, refer to the JBrowse section.
) with hyperlink for opening JBrowse to show editing site in genomic context. For more details on JBrowse, refer to the JBrowse section.
When users search editing sites in the blast page, the icon (![]() ) with hyperlink for opening a new page to show original alignment of a BLAST search.
) with hyperlink for opening a new page to show original alignment of a BLAST search.
When users search editing sites in the pathway page, the corresponding KEGG ortholog and enzyme of edited genes also appears in retrieval result table.
In the retrieval result table, users can click the details icon (![]() ) to open the detail page to show an A-to-I editing site. The detail page contains two sections including basic annotation and editing levels.
) to open the detail page to show an A-to-I editing site. The detail page contains two sections including basic annotation and editing levels.
In the section of basic annotation, users can see species name, genomic position, genomic context and other information including edited gene/mRNA identifier, codon, amino acid and editing effect in CDSs (if any). In addition, If editing occurs in a gene, its cDNA and protein sequence will also apear. In the cDNA sequence, UTR (5'UTR or 3'UTR) and CDS sequence are respectively marked with blue and black, while the edited nucleic acid is marked with red. Similarly, the edited amino acid in protein sequence is marked with red. The editing sites in introns also can be shown in the detail page. The edited intron is displayed in brown flanked by two neighbor exons displayed in black.
In the section of editing levels, a table is used to list BioProjects that contain edited RNAseq samples (A) and a column chart is used to show numbers of edited RNAseq samples in each BioProject (B). In the BioProject table, users can obtain more details of a BioProject by clicking on its identifier with hyperlink to the description page in NCBI. In the column chart, users can switch to another column graph to visually compare the editing levels in various RNAseq samples of BioProject by clicking on corresponding column (C).
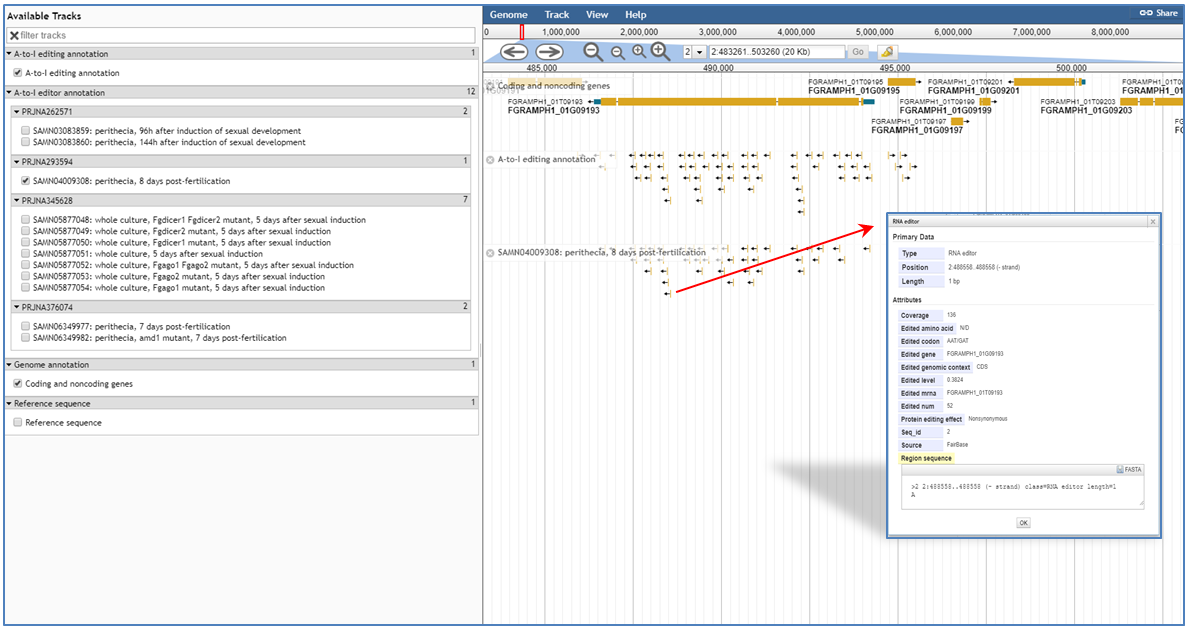
When users submit request in the browse page or click the JBrowse icon(![]() ) in the retrieval result table, JBrowse will be opened for users to explore editing site in the genomic context. In addition to gene annotation and comprehensive A-to-I editing annotation tracks, the tracks of RNAseq samples collected in FairBase also are built in JBrowse and are grouped by their BioProject identifiers. By clicking on editing sites in these tracks, users can retrieve not only the basic annotation information but also the editing levels in corresponding RNAseq samples.
) in the retrieval result table, JBrowse will be opened for users to explore editing site in the genomic context. In addition to gene annotation and comprehensive A-to-I editing annotation tracks, the tracks of RNAseq samples collected in FairBase also are built in JBrowse and are grouped by their BioProject identifiers. By clicking on editing sites in these tracks, users can retrieve not only the basic annotation information but also the editing levels in corresponding RNAseq samples.